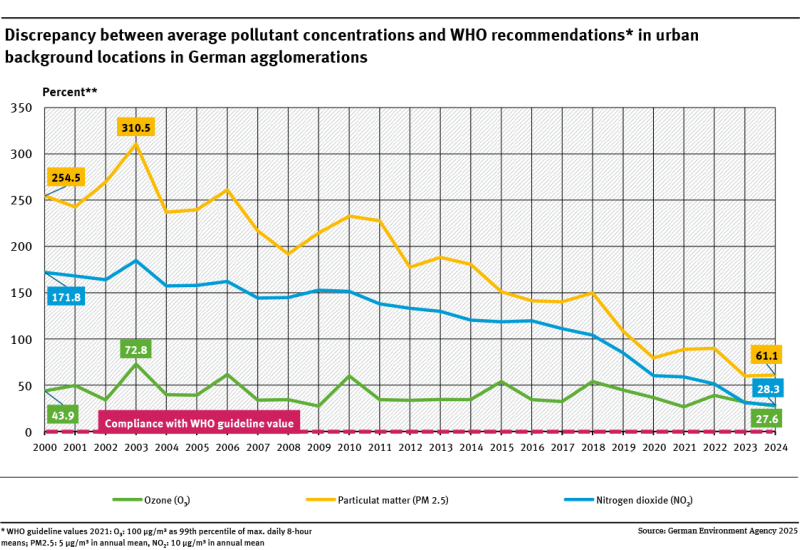
The averaged index of air pollutants fell by 39.5 % between 2005 and 2023.The obligations of the Gothenburg Protocol and the NEC Directive for 2020 were achieved.The challenge to meet the reduction commitments of the European NEC Directive for 2030 differ from substance to substance.Nitrogen oxide emissions need to be reduced significantly to achieve the 2030 goal.For sulphur dioxide, ammonia and... read more
Topics | Umweltbundesamt
 Umweltbundesamt
Umweltbundesamt
Search