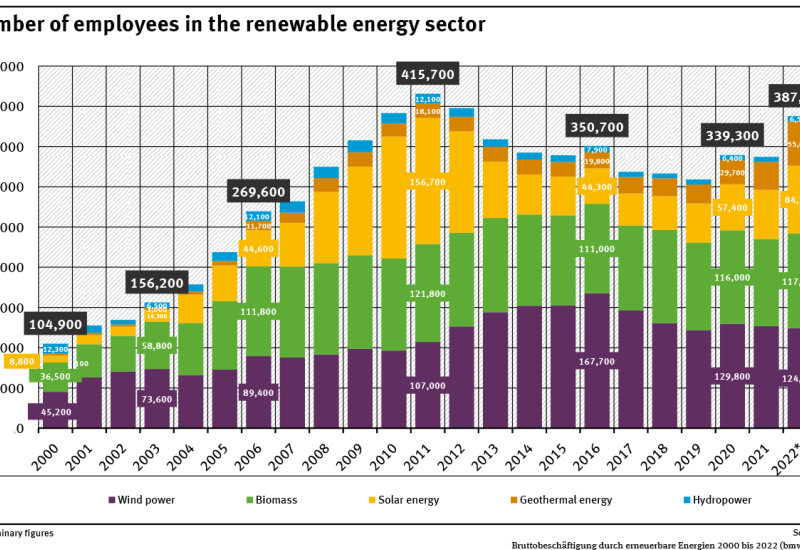
387,700 people worked in the renewable energy sector in 2022.Employment in the renewable energy sector reflects the development of the German market.Strong employment growth until 2011 was followed by a pronounced decline that resulted from the widespread collapse of the domestic photovoltaic industry.Only since 2019, employment has been rising again. read more
indicator
Umwelt-Indikator
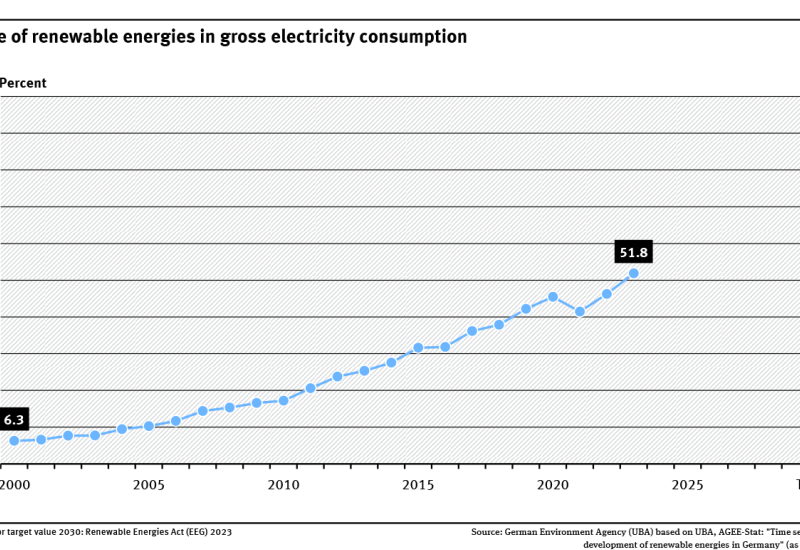
Indicator: Share of renewables in gross electricity consumption
Electricity accounts for around a fifth of the total final energy consumption. This share is set to increase in the future.The share of renewable energies in gross electricity consumption rose from 6.3 % to 51.8 % between 2000 and 2023.The German Renewable Energy Sources Act (EEG) stipulates that the share of renewable energies should increase to at least 80 % by 2030.If Germany achieves its ambit... read more
Indicator: Share of renewables in gross final energy consumption
Gross final energy consumption includes all types of final energy consumption by end consumers, primarily electricity, district heating, fuels and fuels for heat generation.So far, the development has been in line with the previous target of a 30 % share of renewables in 2030.However, as part of the new targets for the EU Renewable Energy Directive, the German target will soon be increased to 40 %... read more
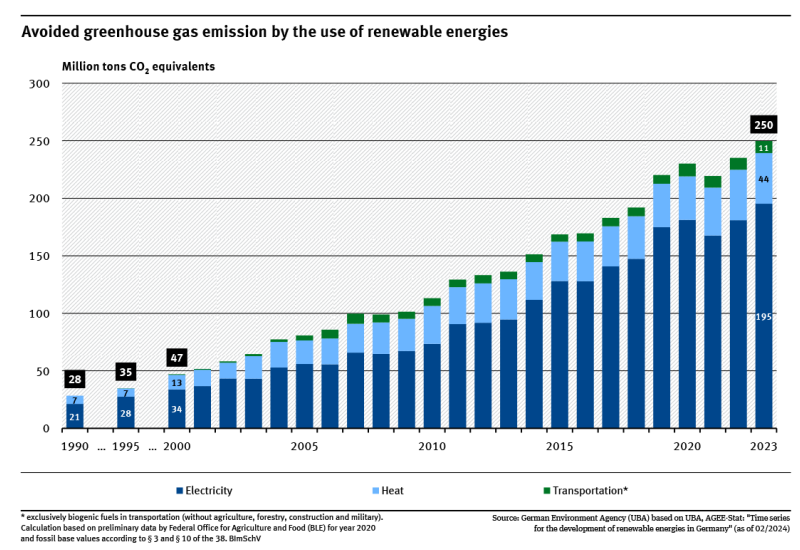
Indicator: Greenhouse gas emissions avoided by renewable energies
Renewables are increasingly replacing fossil fuels in the fields of electricity, heat and transport.More than ¾ of avoided emissions in 2023 were prevented by renewable electricity.The Federal Government intends to considerably expand the share of renewables to further reduce greenhouse gas emissions. read more
Indicator: Primary energy consumption
Primary energy consumption (PEC) in Germany has fallen significantly since the end of the 2000s. It fell by 25 % between 2008 and 2023.According to the Energy Efficiency Act of 2023, PEC is to be reduced by 39% by 2030 compared to 2008.The 'Projection Report 2023' by the German Environment Agency indicates that the measures taken so far will likely be insufficient to achieve these targets.The indi... read more
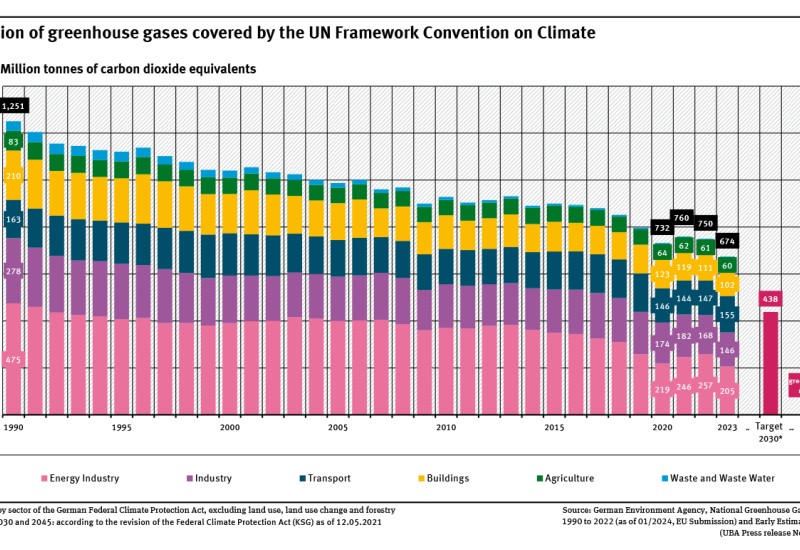
Indicator: Greenhouse gas emissions
According to initial calculations, greenhouse gas emissions in Germany declined by exactly 46.1 % between 1990 and 2023.Germany aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 40 % by 2020 and by at least 65 % by 2030 compared to 1990 emission levels. Complete greenhouse gas neutrality is to be achieved by 2045.In 2023, Germany was well below the target of minus 40 % set for 2020. The targets for 2030... read more
Indicator: Emission of air pollutants
The averaged index of air pollutants fell by 34.4% between 2005 and 2022.The obligations of the Gothenburg Protocol and the NEC Directive for 2020 were achieved.Safely meeting the commitments of the European NEC) Directive for 2030, is a challenge for the German environmental policy.Ammonia emissions must continue to be significantly reduced to achieve this. read more
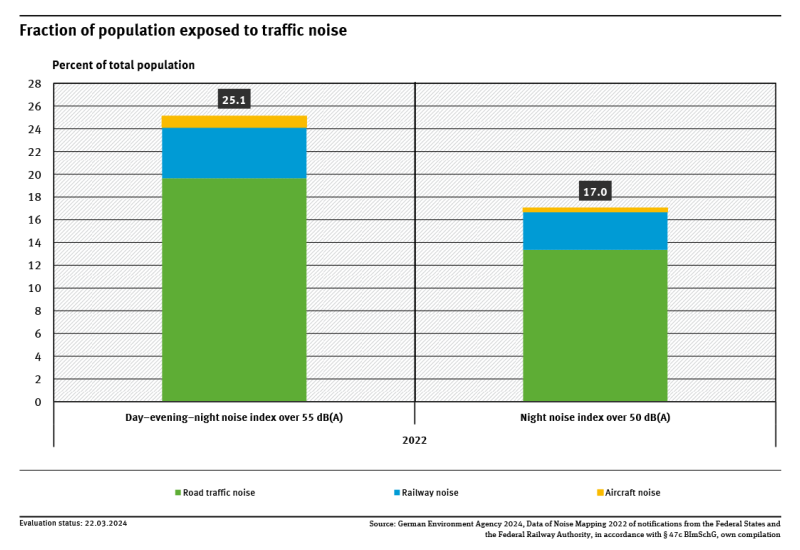
Indicator: Population exposure to traffic noise
According to the 2022 noise mapping, about 17.0 % of the total population was adversely affected by night-time noise.They further showed that 25.1 % of the population was exposed to a noise level of above 55 decibels during the day.The main source of noise is road traffic. Aircraft noise hardly plays a role in the area assessment.Noise that exceeds exposure limits can lead to health problems. read more